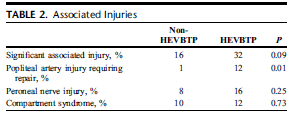
In the HEVBTP group, 32% of the patients were combined with other tissue or structural damage, and 3 patients (12%) had popliteal vascular injury requiring surgical repair.
In contrast, only 16% of patients in the non-HEVBTP group had other injuries, and only 1% required popliteal vascular repair. In addition, 16% of EVBTP patients had partial or complete peroneal nerve injury and 12% had calf compartment syndrome, compared with 8% and 10% of the control group, respectively
Traditional tibial plateau fracture classification systems, such as the Schatzker, Moore, and AO/OTA classifications, are designed to help surgeons identify associated injuries and develop treatment plans
These fractures are usually classified as AO C and Schatzker V or VI
However, the specifics of this type of fracture may be overlooked by this classification, which may leave some patients with unnecessary disease in the presence of severe neurovascular complications
The injury mechanism of HEVBTP is similar to that of anteromedial tibial plateau fracture combined with posterior external complex injury and posterior cruciate ligament rupture
Therefore, for the fracture of the anteromedial tibial plateau, attention should be paid to the injury of the posterolateral side of the knee joint.
In the present study, the injury described in our case was often similar to a compression fracture of the tibial plateau. However, in contrast to soft tissue injuries of the posterolateral or posterior cruciate ligament, the injuries in these cases are bony and are considered tension fractures on the metaphysis or lateral plateau
Clearly, the identification of injury patterns is what allows surgeons to optimally treat fractured patients. Identification is made possible by the simultaneous acquisition of multiplanar imaging and computed tomography to determine the subtleties of the injury.
It is important to recognize the importance of this injury, which is an important related injury.
Moore recognized that certain types of tibial plateau injuries are not isolated but represent a spectrum of injuries that include ligamentous and neurovascular injuries.
Likewise, in this study, hyperextension and varus tibial plateau bicondylar fractures were found to be associated with a 32% higher risk of other injuries, including popliteal vessel injury, peroneal nerve injury, and compartment syndrome.
In conclusion, hyperextension and varus bicondylar tibial plateau fractures are a unique pattern of tibial plateau fractures. The imaging features of this mode are
(1) Loss of normal posterior slope between sagittal plane and tibial articular surface
(2) Tension fracture of the posterior cortex
(3) Compression of the anterior cortex, varus deformity on the coronal view.
Surgeons should recognize that this injury may occur after a low-energy injury mechanism in older adults with a relatively high level of neurovascular injury. The reduction and immobilization strategies described can be used to treat this mode of injury.
Post time: May-16-2022





